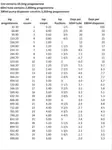
Hormone testing
The advantages of saliva hormone testing...
- Stress-free
- Noninvasive (no needles)
- Less expensive/more convenient for health care provider and patient
- Optimized for collection any time of day/month, any place
- No special processing (eg, centrifugation, ice-packs) prior to shipment
- Hormones stable in saliva for prolonged period of time
- Convenient shipment by regular US mail
- More representative than serum of total bioavailable steroid hormone levels
The disadvantages of saliva hormone testing...
- Technically more challenging: need 10-20 x sensitivity
- Interfering substances-food, beverages
- Saliva easily contaminated with topical hormones on lips or hands
- Spurious results with peridontal disease (more problem with chewing gum)
- Lack of familiarity (serum is gold standard)
- Sublingual use of hormones often leads to inaccurate (high) results
- No proficiency testing (CAP, AAB) that reflects saliva hormone levels
- Topical application of hormones results in saliva levels higher than serum
Please note...
The first figures given below are the Conventional Unit and the second figures are the SI Unit.
The Conventional Unit is generally used in America, whereas the SI Unit is used by the rest of the world. Reference ranges can vary between countries and between labs.
Furthermore some results are given in pg/ml and others in ng/ml, or pmol/L and nmol/L. A pg/pmol is 1000 times smaller than a ng/nmol.
To add to the confusion, if there is only one Unit given, that is the standard the world over. For conversion factors see here.
Many women are told their progesterone and oestrogen levels are 'normal'. But the critical factor is not the LEVELS but the RATIO of progesterone to oestrogen, often written P:E2.
Finding the ratio is easy if saliva tests are performed... just divide the oestrogen result into the progesterone result. An often overlooked complication is that in blood tests, oestrogen is measured in pg/ml and progesterone in ng/ml. A pg is 1000 times smaller than a ng, so divide the oestrogen result by 1000 to convert it to ng. Then divide this into the progesterone result. Here's an example...
If the serum oestrogen result was 250pg/ml and the progesterone 5ng/ml,
first divide...
250 by 1000 = 0.25ng/ml
Then divide...
5 by 0.25 = 20
So the ratio of progesterone to oestrogen is 20:1
From Saliva Tests that we have run, we've found the ratio should be 600:1 to feel well.
Progesterone (serum)
Female (follicular) <1 ng/ml or <3.18 nmol/L
Female (luteal) 5 to 20 ng/ml or 15.9 - 63.6 nmol/L
Postmenopausal <1 ng/l or <3.18 nmol/L
Male <1 ng/ml or <3.18 nmol/L
Pregnancy (serum)
1st trimester 11.2 - 90.0 ng/ml or 35.6 - 286.2 nmol/L
2nd trimester 25.6 - 89.4 ng/ml or 81.4 - 284.29 nmol/L
3rd trimester 48.4 - 425 ng/ml or 153.9 - 1351.5 nmol/L
Oestrone (E1) (serum)
Menopause 30 pg/ml or 111 pmol/L
Princeton Uni: Understanding menopause
Oestradiol (E2) (serum)
Female (premenopausal) 30 - 400 pg/ml or 110.13 - 1468.4 pmol/L
Female (postmenopausal) 0 - 30 pg/ml or 0 - 110.13 pmol/L
Male 10 - 50 pg/ml or 36.71 - 183.55 pmol/L
Oestriol (E3) in pregnant women (serum)
1st trimester Less than 38 ng/mL or 131.7 nmol/L
2nd trimester 38-140 ng/mL or 131.7 - 485.4 nmol/L
3rd trimester 31-460 ng/mL or 107.5 - 1594.8 nmol/L
WebMD Oestrogens
Testosterone - total (serum)
Male 300 - 1200 ng/dL or 10.41 - 41.64 nmol/L
Female 30 - 95 ng/dL or 1.041 - 3.29 nmol/L
Free testosterone (Free testosterone ranges from 1 to 4% of total) - Female
Female 20 - 40 yr 0.6 - 3.1 pg/ml or 20.8 - 107.5 pmol/L
41 - 60 yr 0.4 - 2.5 pg/ml or 13.9 - 86.7 pmol/L
61 - 80 yr 0.2 - 2.0 pg/ml or 6.9 - 69.3 pmol/L
Keratin.com
Free testosterone (Free testosterone ranges from 1 to 4% of total) - Male
Male 20 - 40 years 15.0 - 40.0 pg/ml or 520 - 1387 pmol/L
41 - 60 years 13.0 - 35.0 pg/ml or 451 - 1213 pmol/L
61 - 80 years 12.0 - 28.0 pg/ml or 416 - 971 pmol/L
Keratin.com
Progesterone (saliva)
Female (follicular) 12-100 pg/ml or 38.16 - 318.00 pmol/L
Female (luteal) 75-270 pg/ml or 238.5 - 858.6 pmol/L
Postmenopausal 12-100 pg/ml or 38.16 - 318.00 pmol/L
Male 15-100 pg/ml or 47.70 - 318.00 pmol/L
Oestradiol (saliva)
Female (premenopausal): 1.3-3.3 pg/ml or 4.77 - 12.11 pmol/L
Female (postmenopausal): 0.5-1.7 pg/ml or 1.84 - 6.24 pmol/L
Male: 0.8 - 2.2 pg/ml or 2.94 - 8.08 pmol/L
Testosterone (saliva)
Female all ages 16-55 pg/ml or 0.56 - 1.91 pmol/L
Female ages 16-30 18-55 pg/ml or 0.62 - 1.91 pmol/L
Female ages >30 16-47 pg/ml or 0.56 - 1.63 pmol/L
Male all ages 44-148 pg/ml or 1.53 - 5.14 pmol/L
Male ages 16-30 72-148 pg/ml or 2.50 - 5.14 pmol/L
Male ages 31-50 58-120 pg/ml or 2.01 - 4.16 pmol/L
Male ages 51-70 44-94 pg/ml or 1.53 - 3.26 pmol/L
Male ages >70 30-77 pg/ml or 1.04 - 2.67 pmol/L
Serum hCG levels
(GA (gestational age), occasionally given as LMP (last menstrual period). Please note, this is not taken from time of conception, but from the last menstrual period. If the date of conception is known, take off the days for the follicular phase.
Non-pregnant females or negative test: <5.0 mIU/ml or <5.0 IU/L
3 weeks GA: 5 - 50 mIU/ml or 5 - 50 IU/L
4 weeks GA: 5 - 426 mIU/ml or 5 - 426 IU/L
5 weeks GA: 18 - 7,340 mIU/ml or 17 - 7340 IU/L
6 weeks GA: 1,080 - 56,500 mIU/ml or 1,080 - 56,500 IU/L
7-8 weeks GA: 7,650 - 229,000 mIU/ml or 7,650 - 229,000 IU/L
9-12 weeks GA: 25,700 - 288,000 mIU/ml or 25,700 - 288,000 IU/L
13-16 weeks GA: 13,300 - 254,000 mIU/ml or 13,300 - 254, 000 IU/L
17-24 weeks GA: 4,060 - 165,400 mIU/ml or 4,060 - 165,400 IU/L
25-40 weeks GA: 3,640 - 117,000 mIU/ml or 3,640 - 117,000 IU/L
American Pregnancy Association hCG levels
SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin)
Follicular phase 24 - 200 nmol/L
Luteal phase 48 - 185 nmol/L
Contraceptives 89 - 379 nmol/L
Postmenopausal 46 - 200 nmol/L
Males: 6 - 50 nmol/L
FSH levels
Male.....Before puberty 0-5.0 IU/L
During puberty 0.3-10.0 IU/L
Adult 1.5-12.4 IU/L
Female..Before puberty 0-5.0 IU/L
During puberty 0.3-10.0 IU/L
Menstruating women 3.5-30.0 IU/L
Postmenopausal 40-250 IU/L
Pregnant women too low to measure
LH levels (An LH level higher than FSH is a possible indication of PCOS)
Women
Follicular phase: 1.68-15 IU/L
Midcycle peak: 21.9-56.6 IU/L
Luteal phase: 0.61-16.3 IU/L
Menopause: 14.2-52.3 IU/L
Men: 1.24-7.8 IU/L
Prolactin
Males 2 - 18 ng/mL or 86.96 - 782.60 pmol/L
Non-pregnant females 2 - 29 ng/mL or 86.96 - 1260.86 pmol/L
Pregnant women 10 - 209 ng/mL or 434.78 - 9086.90 pmol/L
Vitamin D (essential test)
The test should be done for 25-hydroxyvitamin D, also called calcidiol
The following list gives an indication of levels of vitamin D found in the blood
Sufficient 50-100ng/ml or 124.80-249.60 nmol/L
Hypovitaminosis less than 30ng/ml or 75 nmol/L
Deficiency less than 25ng/ml or 62.4nmol/L
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
Normal values are 10 - 55 pg/mL or 10 - 55 ng/L
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone or thyrotrophin)
Normal values are 0.4 - 4.0 mIU/L
T3 total (triiodothyronine)
Normal values are 100 - 200 ng/dL or 1.54 - 3.08 nmol/L
T4 total (thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine)
Normal values are 4 to 11 mcg/dL or 60 - 140 nmol/L
Iodine
Median Population Urinary Iodine Values (g/L)
Severe deficiency <20
Moderate deficiency 20-49
Mild deficiency 50-99
Optimal 100-199
More than adequate 200-299
Possible excess >299
CRP (C-reactive protein, a marker for inflammation)
The level of CRP rises when there is inflammation throughout the body, normally none should be found
Levels if found, vary from <1.0mg/L to >3.0mg/L
And
Late pregnant women, mild inflammation and viral infections 1040 mg/L
Active inflammation, bacterial infection 40200 mg/L
Severe bacterial infections and burns >200 mg/L
Homocysteine (a marker for inflammation)
12-19 YEARS >/= 60 YEARS Cut off for high levels
Male 4.3-9.9 umol/L 5.9-15.3 umol/L >/=11.4 umol/L
Female 3.3-7.2 umol/L 4.9-11.6 umol/L >/=10.4 umol/L
MDA (Malondialdehyde, a marker for oxidative stress/inflammation, it forms when lipids are oxidised)
Standard Range: 1.0 - 4.0 mM
Northwest Life Science Specialties
Cholesterol
Total cholesterol
Desirable <200 mg/dL or <5.2 mmol/L
Borderline high 200 to 239 mg/dL or 5.2 mmol/L to 6.2 mmol/L
High risk 240 mg/dL and higher or 6.2 mmol/L
HDL cholesterol
Levels should be >40 mg/dL or >1.04 mmol/L
Men are at particular risk if their HDL is below 37 mg/dL or 0.96 mmol/L
Women are at particular risk if their HDL is below 47 mg/dL or 1.22 mmol/L
LDL cholesterol
Optimal < 100 mg/dL or <2.59 mmol/L
Near Optimal 100 - 129 mg/dL or 2.59 mmol/L - 3.34 mmol/L
Borderline High 130 - 159 mg/dL or 3.38 mmol/L - 4.12 mmol/L
High 160 - 189 mg/dL or 4.14 mmol/L - 4.90 mmol/L
Very High 190 mg/dL and higher or 4.92 mmol/L
Triglycerides
Normal < 150 mg/dL or <1.79 mmol/L
Borderline High 150 - 199 mg/dL or 1.79 mmol/L - 2.25 mmol/L
High 200 - 499 mg/dL or 2.26 mmol/L - 5.64 mmol/L
Very High 500 mg/dL or above or 5.65 mmol/L
DHEA-sulphate (Dehydroepiandrosterone-sulphate)
Ages 18 - 19 145 - 395 ug/dL or 503.2 - 1370.7 nmol/L
Ages 20 - 29 65 - 380 ug/dL or 225.6 - 1318.6 nmol/L
Ages 30 - 39 45 - 270 ug/dL or 156.2 - 936.0 nmol/L
Ages 40 - 49 32 - 240 ug/dL or 111.0 - 832.8 nmol/L
Cortisol
Normal values for a blood sample taken at 8 in the morning are 6 - 23 ug/dL or 165 - 635 nmol/L.
During the afternoon they are 3-16 mcg/dL or 83-441 nmol/L.
Normally, cortisol levels rise and fall during the day, repeating on a 24-hour cycle (diurnal variation). Highest levels are at about 6 - 8 a.m. and lowest levels are at about midnight.
Physical and emotional stress can increase cortisol levels, because during the normal stress response, the pituitary gland increases its release of ACTH.
Higher than normal cortisol levels are expected in women who take oestrogen or birth control pills.
Glucose (fasting)
Normal levels <100 mg/dL or <5.5 mmol/L
Levels between 100 - 125 mg/dL or 5.5 mmol/L - 6.9 mmol/L may indicate impaired fasting glucose or insulin resistance
Diabetes >126 mg/dL or >6.9 mmol/L
Insulinoma (a pancreatic tumour which causes excessive secretion of insulin)...
women <40 mg/dL or <2.2 mmol/L
men <50 mg/dL or <2.8mmol/L
Insulin resistance
There is no single test for IR, but the following are often tested...
Blood pressure equal to or higher than 130/85 mmHg
Fasting blood glucose equal to or higher than 100 mg/dL or 5.55 mmol/L
Insulin levels >20 IU/mL or 140 pmol/L
normal range 2.0-20 IU/mL or 14-140 pmol/L
although many believe it should be <10 IU/mL or 70 pmol/L
Elevated CRP - see above for more info
Large waist circumference 35 inches or 87.5cm or more
Low HDL cholesterol Under 50 mg/dL or 1.3 mmol/L
Triglycerides equal to or higher than 150 mg/dL or 1.79 mmol/L
Lab Tests Online - Understanding insulin resistance
Glycated or glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c or A1C)
Normal 20-40 mmol/mol or 4%-5.8%
Liver Function tests
Wikipedia Scroll through the contents and click on Liver Function
Medline Scroll through the list to the desired test
 Migraines aren’t just intense headaches — they’re a systemic neurological crisis that disrupts your senses, drains your energy, and derails your life. What most people don’t realize is that women are…
Migraines aren’t just intense headaches — they’re a systemic neurological crisis that disrupts your senses, drains your energy, and derails your life. What most people don’t realize is that women are… Psoriasis is commonly seen as a skin problem — red, scaly patches that itch and flare without warning — but research shows the real driver may be hormonal imbalance deep inside the body, especially lo…
Psoriasis is commonly seen as a skin problem — red, scaly patches that itch and flare without warning — but research shows the real driver may be hormonal imbalance deep inside the body, especially lo… Low libido—whether described as poor sexual desire, low arousal, or hypoactive sexual desire disorder—is a common and complex issue affecting both men and women, shaped by physical, endocrinologic, ne…
Low libido—whether described as poor sexual desire, low arousal, or hypoactive sexual desire disorder—is a common and complex issue affecting both men and women, shaped by physical, endocrinologic, ne…